삼각형 그리기
Android에서 OpenGL ES 2.0으로 삼각형을 정의하고, SurfaceView에 그려본다.
우선 OpenGL ES는 3차원 공간에서 좌표로 객체를 그린다.
객체는 각 점(vertex)들을 따라가면서 만들어지는 면(fragment)를 그리는 방식이고, 좌표는 반시계 방향 순서로 정의한다.
OpenGL ES에서는 (0, 0, 0)이 프레임의 중앙, (1, 1, 0)이 프레임의 오른쪽 위이다.
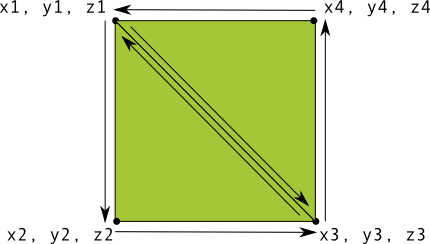
자세한 내용은 공식 문서에서 확인할 수 있으며, 삼각형을 정의한는 코드는 아래와 같다
공식 예제 코드에서는 적당한 삼각형이지만, 아래 코드는 정삼각형으로 수정하였다.
도형을 그리는 데 필요한 것:
Vertex Shader - 도형의 꼭짓점을 렌더링하는 OpenGL ES 그래픽 코드
Fragment Shader - 색상 또는 질감으로 도형의 면을 렌더링하는 OpenGL ES 코드
Program - 하나 이상의 도형을 그리는 데 사용할 셰이더가 포함된 OpenGL ES 객체
Vertex Shader 와 Fragment Shader 는 코드이다. 따라서 컴파일 할 GLSL(OpenGL Shading Language) 코드로 작성된다.
각 도형들이 Program 을 가지고 있고, 렌더러(Renderer)가 나중에 이 프로그램을 렌더링에 추가하여 객체를을 그릴 것이다.
SurfaceView에서 Renderer를 통하여 OpenGL ES 객체를 그리는 것이다.
두 셰이더(Shader)와 프로그램(Program), 그리고 렌더러(Renderer)까지 예제를 잘 따라했다면 삼각형이 그려지는 것을 볼 수 있다.

그런데 삼각형이 찌그러져 있을 것이다. 분명 정삼각형을 정의했는데!
그 이유는 프로젝션(Projection)과 카메라 뷰(Camera View)가 없어서 그렇다.
[그림 2]에서 우리가 그래픽을 그리는 GLSurfaceView는 [그림 3]의 오른쪽처럼 뷰 포트의 크기가 변한다.
이것을 GLSurfaceView의 너비와 높이를 보고 다시 좌표를 조정해야하는데, 투영(Projection)시키기 위해서 가상의 카메라 위치를 잡아야한다.
[그림 3]을 보면 좌표계는 [-1.0, 1.0] 사이의 값으로 표현된다. 찌그러진 것을 복구하기 위해서 좌표의 아래(bottom)와 위(top)를 -1과 1로 했을 때, 왼쪽(left)과 오른쪽(right)의 비율만 조정하는 것이다.
위 그림에서 Near와 Far가 아주 가까워 착 붙어있는 뷰 포트에 투영시킨다고 생각하면 되겠다.
Matrix.frustumM() 함수는 그렇게 비율을 조정하는 행렬(Matrix)을 첫 번째 인자에 넣어준다. 우린 이 행렬(Matrix)로 객체를 투영시킬 수 있다.

가상의 카메라 뷰인 mViewMatrix 를 적절한 위치에 두고, onSurfaceChanged 에서 만들어진 투영 행렬 mProjectionMatrix 과 합쳐서 그것으로 다시 삼각형을 그린다.

Matrix.setLookAtM 의 파라미터는 레퍼런스와 위 그림을 함께 보면 좋다.
Code
https://github.com/joonas-yoon/android-opengl-example/tree/142dcbab1815e6ec25f5954493a07c088f27552c
Links
Last updated